- Clone
- XMG1.2 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Interferon-γ, Immune interferon, Type II interferon, T cell interferon, Macrophage-activating factor (MAF)
- Isotype
- Rat IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
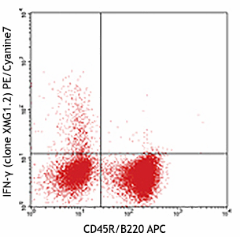
-

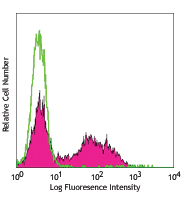
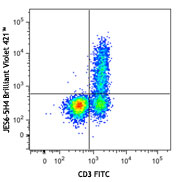
PMA/Ionomycin-stimulated (6hrs) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with B220 (RA3-6B2) APC and XMG1.2 PE/Cyanine7
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 505825 | 25 µg | 106€ | ||||
| 505826 | 100 µg | 243€ | ||||
IFN-γ is a potent multifunctional cytokine which is secreted primarily by activated NK cells and T cells. Originally characterized based on anti-viral activities, IFN-γ also exerts anti-proliferative, immunoregulatory, and proinflammatory activities. IFN-γ can upregulate MHC class I and II antigen expression by antigen-presenting cells.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- E. coli-expressed, recombinant mouse IFN-γ
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PE/Cyanine7 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
ICFC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by intracellular immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤1.0 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
ELISA1-4,11,14 or ELISPOT5 Detection: The biotinylated XMG1.2 antibody is useful as a detection antibody for a sandwich ELISA or ELISPOT assay, when used in conjunction with purified R4-6A2 antibody (Cat. No. 505702/505706) as the capture antibody and recombinant mouse IFN-γ (Cat. No. 575309) as the standard.
ELISA or ELISPOT Capture: The purified XMG1.2 antibody is useful as a capture antibody for a sandwich ELISA or ELISPOT assay, when used in conjunction with biotinylated R4-6A2 antibody (Cat. No. 505704) as the detection antibody and recombinant mouse IFN-γ (Cat. No. 575309) as the standard. The LEAF™ purified antibody is suggested for ELISPOT capture (Cat. No. 505812).
Flow Cytometry7,8,12,13,16: The fluorochrome-labeled XMG1.2 antibody is useful for intracellular immunofluorescent staining and flow cytometric analysis to identify IFN-γ-producing cells within mixed cell populations.
Neutralization1-3,9,10: The XMG1.2 antibody can neutralize the bioactivity of natural or recombinant IFN-γ. The LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin <0.1 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for neutralization of mouse IFN-γ bioactivity in vivo and in vitro (Cat. No. 505812). For in vivo studies or highly sensitive assays, we recommend Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Cat. No. 505834) with a lower endotoxin limit than standard LEAF™ purified antibodies (Endotoxin <0.01 EU/µg).
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: Western blotting, immunohistochemical staining of frozen tissue sections6,22,23, and immunocytochemistry.
Note: For testing mouse IFN-γ in serum, plasma or supernatant, BioLegend's ELISA Max™ Sets (Cat. No. 430801 to 430806) are specially developed and recommended. - Additional Product Notes
-
BioLegend is in the process of converting the name PE/Cy7 to PE/Cyanine7. The dye molecule remains the same, so you should expect the same quality and performance from our PE/Cyanine7 products. Please contact Technical Service if you have any questions.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Abrams J, et al. 1992. Immunol. Rev. 127:5. (ELISA, Neut)
- Sander B, et al. 1993. J. Immunol. Meth. 166:201. (ELISA, Neut)
- Abrams J, et al. 1995. Curr. Prot. Immunol. John Wiley and Sons, New York. Unit 6.20. (ELISA, Neut)
- Yang X, et al. 1993. J. Immunoassay 14:129. (ELISA)
- Klinman D, et al. 1994. Curr. Prot. Immunol. John Wiley and Sons, New York. Unit 6.19. (ELISPOT)
- Sander B, et al. 1991. Immunol. Rev. 119:65. (IHC)
- Ferrick D, et al. 1995. Nature 373:255. (FC)
- Ko SY, et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 175:3309. (FC) PubMed
- Peterson KE, et al. 2000. J. Virol. 74:5363. (Neut)
- DeKrey GK, et al. 1998. Infect. Immun. 66:827. (Neut)
- Dzhagalov I, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:2113. (ELISA)
- Lawson BR, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:5366. (FC)
- Lee JW, et al. 2006. Nature Immunol. 8:181. (FC) PubMed
- Xu G, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:5358. (ELISA) PubMed
- Montfort M, et al.2004. J. Immunol. 173:4084. PubMed
- Haring JS, et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 180:2855. (FC) PubMed
- Jordan JM, et al. 2008. Infect Immun. 76:3717. PubMed
- Tonkin DR, et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 181:4516. PubMed
- Charles N, et al. 2010. Nat. Med. 16:701. (FC) PubMed
- Cui Y, et al. 2009. Invest. Ophth. Vis. Sci. 50:5811. (FC) PubMed
- Mykkanen OT, et al. 2014. PLoS One. 9:114790. PubMed
- Yokogawa M, et al. 2013. Mol. Carcinog. 52:760. (IHC)
- Mottram PL, et al. 1998. J Immunol. 161:602. (IHC)
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_1595591 (BioLegend Cat. No. 505825)
AB_2295770 (BioLegend Cat. No. 505826)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Cytokine; dimer; 40-80 kD (Mammalian)
- Bioactivity
- Antiviral/antiparasitic activities; inhibits proliferation; enhances MHC class I and II expression on APCs
- Cell Sources
- CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, NK cells
- Cell Targets
- T cells, B cells, macrophages, NK cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts
- Receptors
- IFN-γRα (CDw119) dimerized with IFN-γRβ (AF-1)
- Cell Type
- Tregs
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Immunology, Neuroinflammation, Neuroscience
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Fitzgerald K, et al. Eds. 2001. The Cytokine FactsBook. Academic Press, San Diego.
2. De Maeyer E, et al. 1992. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 4:321.
3. Farrar M, et al. 1993. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 11:571.
4. Gray P, et al. 1987. Lymphokines 13:151. - Regulation
- Upregulated by IL-2, FGF-basic, EGF; downregulated by 1-α-25-Dihydroxy vitamin D3, dexamethasone
- Gene ID
- 15978 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about IFN-gamma on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All IFN-γ Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
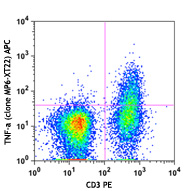
APC anti-mouse IFN-γ

PMA/Ionomycin-stimulated (6hrs) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes st... -
Biotin anti-mouse IFN-γ
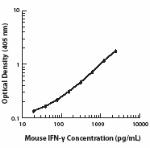
-
FITC anti-mouse IFN-γ


-
PE anti-mouse IFN-γ

PMA/Ionomycin-stimulated BALB/c T-cells were stained with CD... -
Purified anti-mouse IFN-γ

-
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse IFN-γ

PMA+Ionomycin-stimulated (6hrs) Balb/c mouse splenocytes sur... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse IFN-γ
-
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse IFN-γ
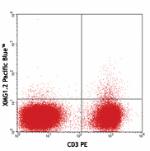
PMA and Ionomycin-stimulated (6hrs) BALB/c splenocytes stain... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse IFN-γ

PMA/Ionomycin-stimlated ( 6hrs ) C57BL/6 splenocytes surface... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse IFN-γ
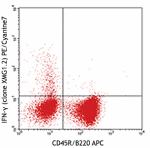
PMA/Ionomycin-stimulated (6hrs) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes st... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse IFN-γ

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stimulated with PMA + Ionomyc... 
-
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse IFN-γ

PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocyt... -
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse IFN-γ

-
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse IFN-γ
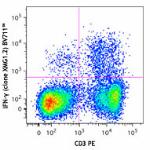
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocyt... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse IFN-γ

PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocyt... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse IFN-γ

PMA+ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (6 hours,... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse IFN-γ

PMA+ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (6 hours,... -
Purified anti-mouse IFN-γ (Maxpar® Ready)
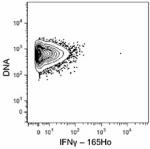
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were incubated for 6 hours in medi... 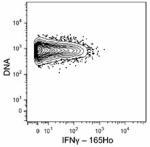
-
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse IFN-γ

PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocyt... 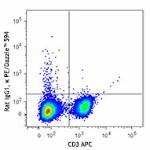
-
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse IFN-γ

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stimulated with Cell Activati... 
-
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse IFN-γ
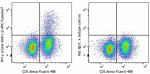
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stimulated with Cell Activati... -
GoInVivo™ Purified anti-mouse IFN-γ
-
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse IFN-γ
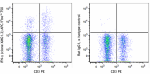
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stimulated with PMA+ Ionomycin in ... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse IFN-γ
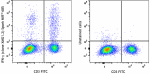
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stimulated with PMA + Ionomycin in... -
Brilliant Violet 750™ anti-mouse IFN-γ
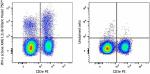
PMA+ ionomycin stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (6 hours...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 












Follow Us