- Clone
- 17A2 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- T cell antigen receptor complex, T3
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
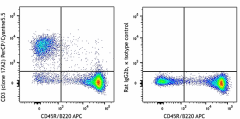
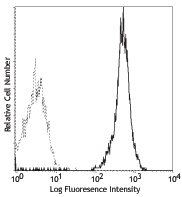
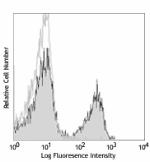
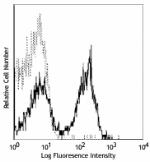
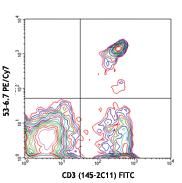
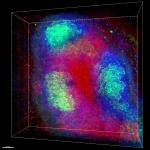
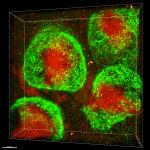
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 APC and CD3 (clone 17A2) PerCP/Cyanine5.5 (left) or Rat IgG2b, ? PerCP/Cyanine5.5 isotype control (right).
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100217 | 25 µg | £81 | ||||
| 100218 | 100 µg | £221 | ||||
CD3, also known as T3, is a member of the Ig superfamily and primarily expressed on T cells, NK-T cells, and at different levels on thymocytes during T cell differentiation. CD3 is composed of CD3ε, δ, γ and ζ chains. It forms a TCR complex by associating with TCR α/β or γ/δ chains. CD3 plays a critical role in TCR signal transduction, T cell activation, and antigen recognition by binding the peptide/MHC antigen complex
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- γδTCR-positive T-T hybridoma D1
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PerCP/Cyanine5.5 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is =1.0 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
* PerCP/Cyanine5.5 has a maximum absorption of 482 nm and a maximum emission of 690 nm. - Application Notes
-
Additional reported application (for relevant formats) include: spatial biology (IBEX)1,2.
- Additional Product Notes
- BioLegend is in the process of converting the name PerCP/Cy5.5 to PerCP/Cyanine5.5. The dye molecule remains the same, so you should expect the same quality and performance from our PerCP/Cyanine5.5 products. Contact Technical Service if you have any questions.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) - Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_1595597 (BioLegend Cat. No. 100217)
AB_1595492 (BioLegend Cat. No. 100218)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Ig superfamily, CD3/TCR, 20 kD
- Distribution
-
Thymocytes (differentiation dependent), mature T cells, NK-T cells
- Function
- Antigen recognition, TCR signal transduction, T cell activation
- Ligand/Receptor
- Peptide antigen/MHC-complex
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay A, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. Davis MM. 1990. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59:475.
3. Weiss A, et al. 1994. Cell 76:263. - Gene ID
- 12502 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD3 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
- How stable is PerCP/Cyanine5.5 tandem as compared to PerCP alone?
-
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 is quite photostable and also better than PerCP alone in withstanding fixation.
Other Formats
View All CD3 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
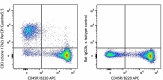
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
FITC anti-mouse CD3

C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with 17A2 FITC and 145-2C11 PE -
PE anti-mouse CD3
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 17A2 PE -
Purified anti-mouse CD3
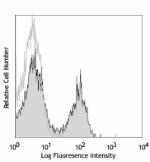
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with purified 17A2, follow... 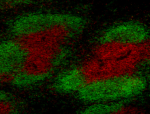
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 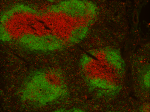
Fresh, frozen mouse spleen was stained with purified CD3 clo... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD3
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 17A2 Alexa Fluor® 647 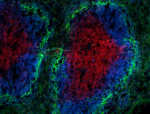
Dissected C57/B6 mouse spleen was immersed in 4% paraformal... 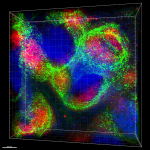
Formalin-fixed, 400 micron-thick mouse spleen section was bl... 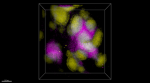
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 μm-thick mouse spleen secti... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD3
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 17A2 Alexa Fluor® 488 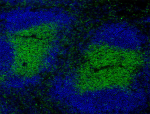
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... Formalin-fixed, 300 micron-thick mouse spleen section was bl... 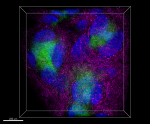
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 μm-thick mouse spleen secti... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD3
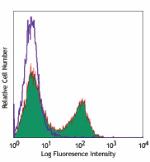
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with Pacific Blue™ 1... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse CD3
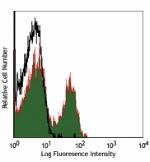
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 17A2 Alexa Fluor® 700 -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD3
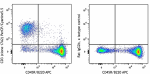
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 APC and CD3... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD3
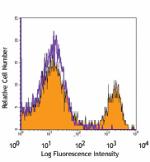
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with 17A2 PE/Cyanine7 -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD3
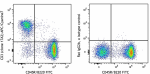
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 FITC and CD... -
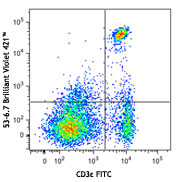
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD3

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD19 APC and CD3... 
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyd... 
-
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-mouse CD3
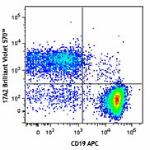
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD19 APC and CD3... 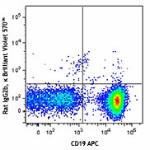
-
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse CD3

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD19 APC and CD3... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse CD3

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD19 APC and CD3... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse CD3
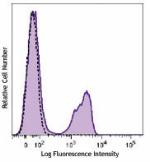
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 (clone 17A2)... -
APC anti-mouse CD3
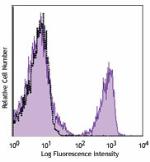
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 (clone 17A2)... -
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD3
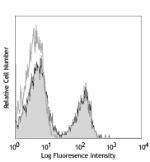
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with Ultra-LEAF™ purified ... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD3

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD19 APC and CD3... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse CD3
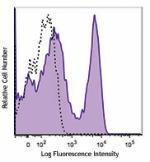
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 (clone 17A2)... 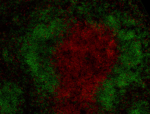
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... Formalin-fixed, 300 micron-thick mouse spleen section was bl... 
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 μm-thick mouse spleen secti... 
Mice were injected subcutaneously with sheep red blood cells... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse CD3
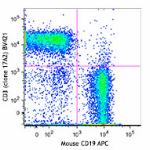
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD19 APC and CD3 (clon... 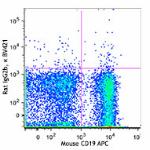
-
Biotin anti-mouse CD3

C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD19 APC and biotinyla... 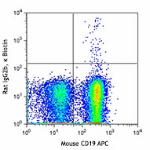
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD3
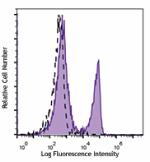
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 (clone 17A2)... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD3
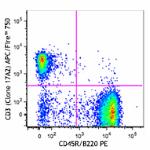
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 PE and CD3 ... 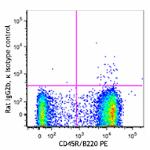
-
Brilliant Violet 750™ anti-mouse CD3
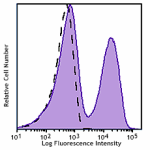
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 (clone 17A2)... -
TotalSeq™-A0182 anti-mouse CD3
-
TotalSeq™-B0182 anti-mouse CD3
-
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-mouse CD3
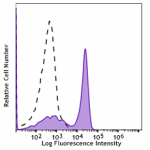
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 (clone 17A2)... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse CD3
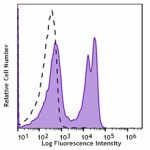
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 (clone 17A2)... -
TotalSeq™-C0182 anti-mouse CD3
-
APC/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse CD3
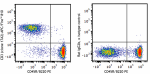
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 PE and CD3 ... -
PE/Fire™ 640 anti-mouse CD3
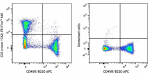
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 APC and CD3... -
Spark YG™ 570 anti-mouse CD3
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... -
PE/Fire™ 700 anti-mouse CD3
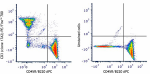
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 APC and CD3... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD3
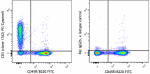
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse/human CD45R... -
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-mouse CD3 Antibody
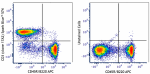
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD45R/B220 ... -
Spark Violet™ 423 anti-mouse CD3
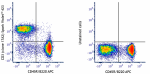
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD45R/B220 ... -
PE/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse CD3
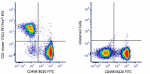
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse/human CD45R... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse CD3
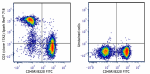
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse/human CD45R... -
Spark UV™ 387 anti-mouse CD3
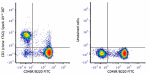
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD45R/B220 ...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us